Weight loss injections have emerged as a notable option for individuals seeking to manage their weight more effectively. These treatments, which typically involve the administration of hormones or other substances, can offer significant benefits, but they also come with potential risks that warrant careful consideration. One of the most commonly discussed types of weight loss injections is those involving glucagon-like peptide-1 GLP-1 agonists, such as semaglutide and liraglutide. These medications mimic the effects of a naturally occurring hormone that helps regulate appetite and glucose metabolism. By activating GLP-1 receptors, these injections can lead to reduced hunger and increased feelings of fullness, which can help individuals consume fewer calories and achieve weight loss. Clinical studies have shown that people using GLP-1 agonists can experience substantial weight loss, sometimes exceeding 10% of their body weight over several months. This level of weight loss is often considered clinically significant and can lead to improvements in associated health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
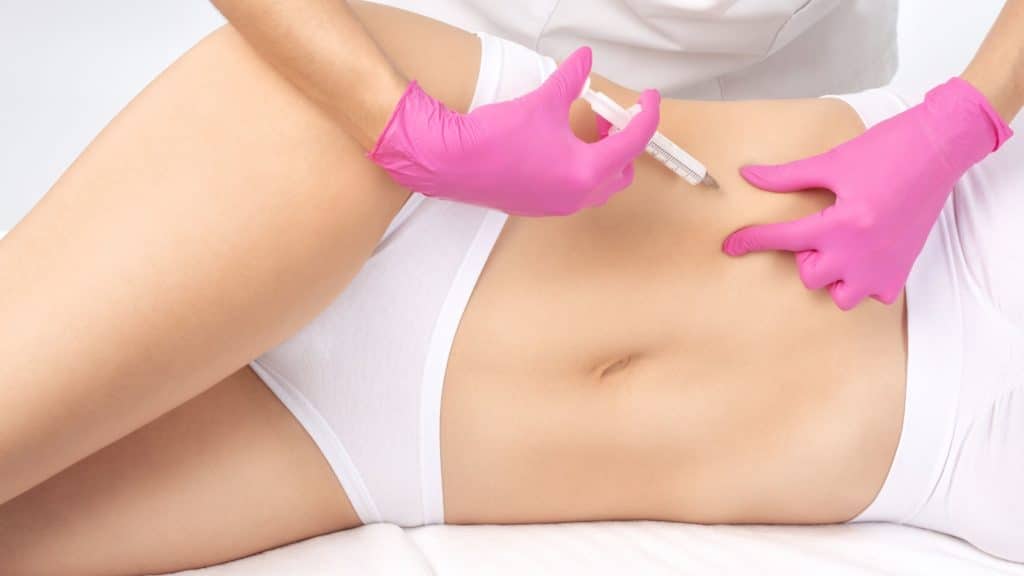 Additionally, weight loss injections can offer a more convenient alternative to lifestyle changes alone. For many individuals, achieving and maintaining weight loss through diet and exercise alone can be challenging. Injections can provide a supplementary tool that, when combined with a healthy lifestyle, may enhance overall weight management efforts. This combination approach can be particularly beneficial for those who have struggled with weight loss despite their best efforts. However, the use of weight loss injections is not without potential risks. Side effects can vary depending on the specific medication, but common issues include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. More serious, though less common, side effects might include pancreatitis, gallbladder problems, or kidney issues. The long-term effects of using these medications are still being studied, and their safety profiles may evolve as more data become available.
Additionally, weight loss injections can offer a more convenient alternative to lifestyle changes alone. For many individuals, achieving and maintaining weight loss through diet and exercise alone can be challenging. Injections can provide a supplementary tool that, when combined with a healthy lifestyle, may enhance overall weight management efforts. This combination approach can be particularly beneficial for those who have struggled with weight loss despite their best efforts. However, the use of weight loss injections is not without potential risks. Side effects can vary depending on the specific medication, but common issues include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. More serious, though less common, side effects might include pancreatitis, gallbladder problems, or kidney issues. The long-term effects of using these medications are still being studied, and their safety profiles may evolve as more data become available.
Furthermore, weight loss injections are typically expensive, and not all insurance plans may cover them. This cost factor can make them inaccessible for some individuals, limiting their use to those who can afford the out-of-pocket expense or who have adequate insurance coverage. It is also crucial for individuals to use weight loss injections under medical supervision Schedule you appointment today. A healthcare provider can assess whether this type of treatment is appropriate based on an individual’s health history and current condition. Self-administering these injections without professional guidance can lead to complications or inadequate results. In summary, weight loss injections can offer significant benefits, such as substantial weight loss and improvements in related health conditions. They can serve as a valuable tool for those who struggle to lose weight through conventional methods. However, potential risks and side effects, along with considerations of cost and medical oversight, highlight the importance of a comprehensive approach to weight management that includes professional guidance and lifestyle modifications.